Product docs and API reference are now on Akamai TechDocs.
Search product docs.
Search for “” in product docs.
Search API reference.
Search for “” in API reference.
Search Results
results matching
results
No Results
Filters
Preparing Your Azure PostgreSQL Database for Logical Replication to Linode Managed Database
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
Logical replication continuously synchronizes database tables, allowing you to prepare the destination database in advance. This approach minimizes downtime when you switch application traffic and retire the source database.
This guide explains how to prepare an Azure Database for PostgreSQL for logical replication to a Linode Managed Database. Follow this guide before returning to the Logical Replication to a Linode Managed PostgreSQL Database guide to create the subscription on Akamai Cloud.
Follow the steps in this guide to:
- Configure your Azure Database instance to support logical replication.
- Ensure secure network access from Linode.
- Create a dedicated replication user.
- Set up a publication for the tables you wish to replicate.
After completing these steps, return to Logical Replication to a Linode Managed PostgreSQL Database to configure the subscriber and finalize the setup.
Before You Begin
Follow the Logical Replication to a Linode Managed PostgreSQL Database guide up to the Prepare the Source Database for Logical Replication section to obtain the public IP address or CIDR range of your Linode Managed Database.
Ensure your Azure account has permissions to modify PostgreSQL server parameters, networking settings, and firewall rules.
Install and authenticate the Azure CLI on your local machine:
az login az account set --subscription YOUR_AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID
Placeholders and Examples
The following placeholders and example values are used in commands throughout this guide:
| Parameter | Placeholder | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Server Name | AZURE_SERVER_NAME | source-database |
| Azure Resource Group | AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP | pg-repl-rg |
| Destination IP Address | DEST_IP | 172.232.188.122 |
| Source Hostname | SOURCE_HOST | source-database.postgres.database.azure.com |
| Source Port | SOURCE_PORT | 5432 |
| Source Username | SOURCE_USER | azureadmin |
| Source Database | SOURCE_DB | postgres |
| Source Password | SOURCE_PASSWORD | thisismysourcepassword |
| Replication Username | REPL_USER | linode_replicator |
| Replication Password | REPL_PASSWORD | thisismyreplicatorpassword |
| Publication Name | PUBLICATION_NAME | my_publication |
Replace these placeholders with your own connection details when running commands in your environment.
Additionally, the examples used in this guide assume the source database contains three tables (customers, products, and orders) that you want to replicate to a Linode Managed Database.
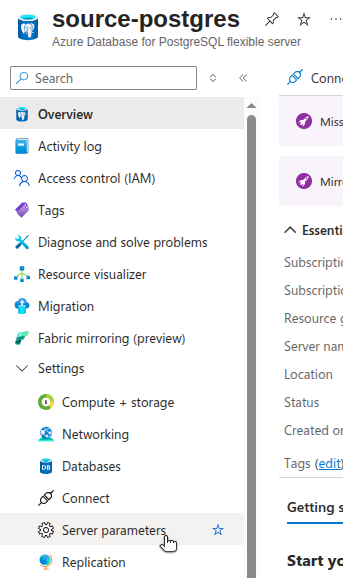
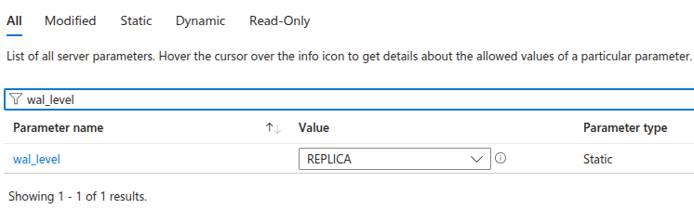
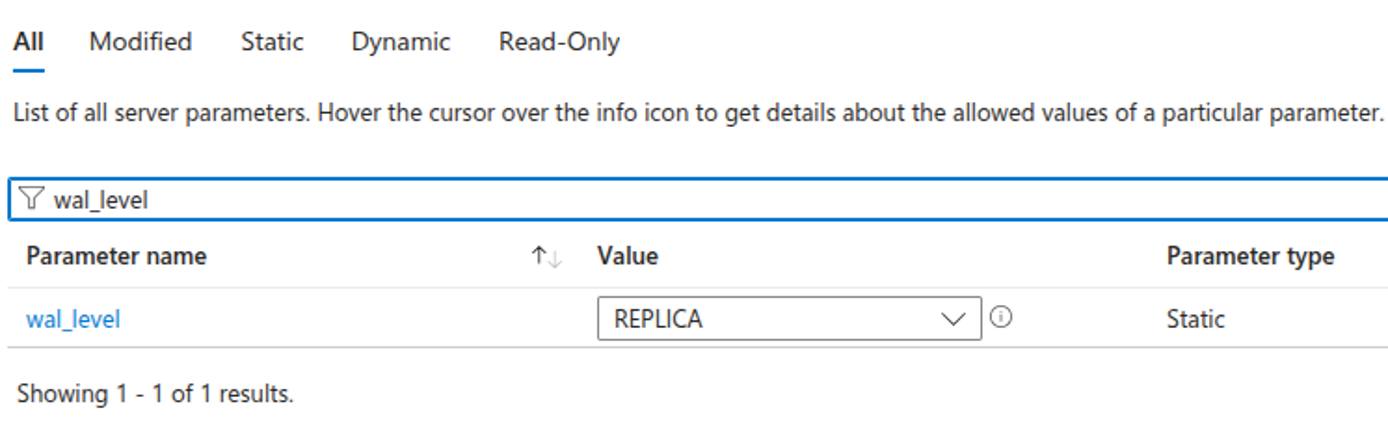
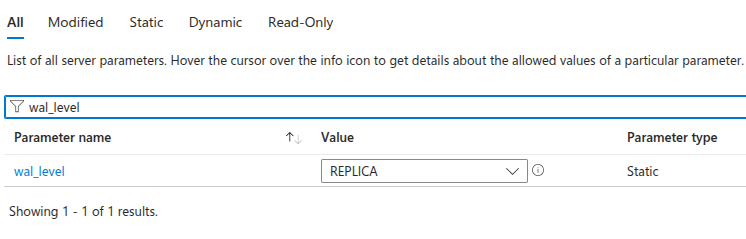
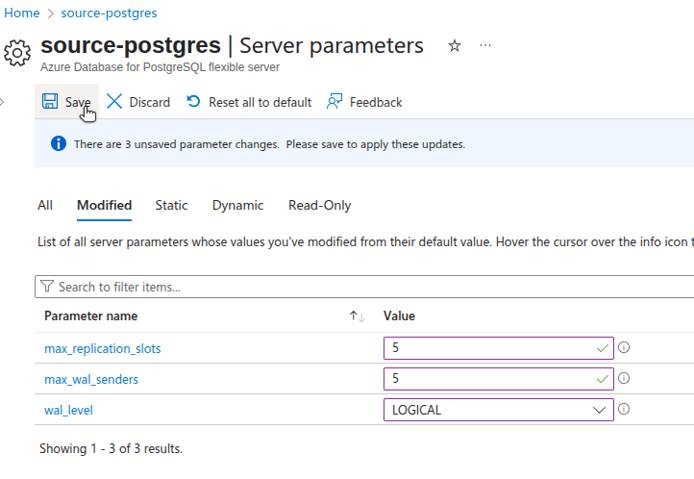
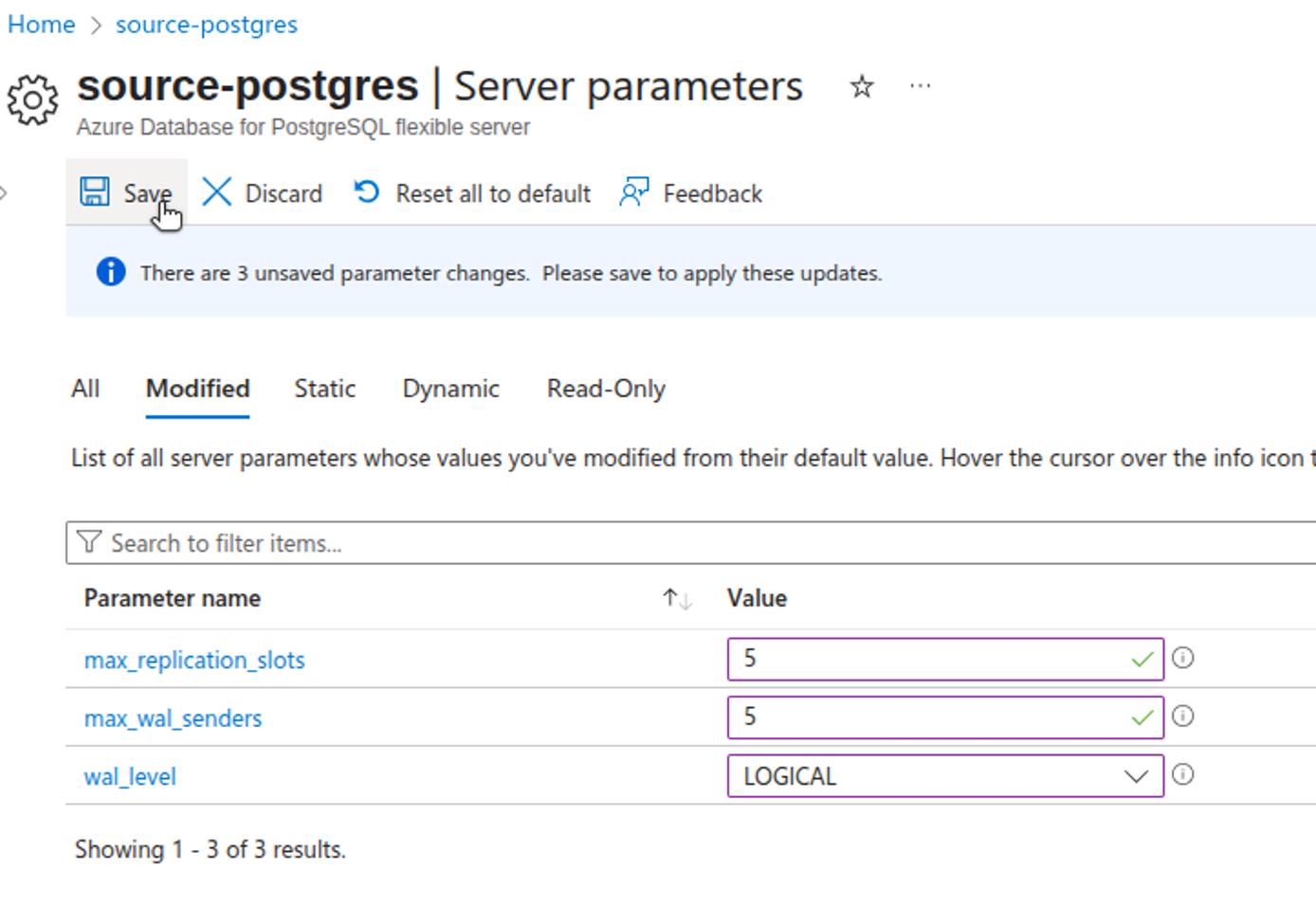
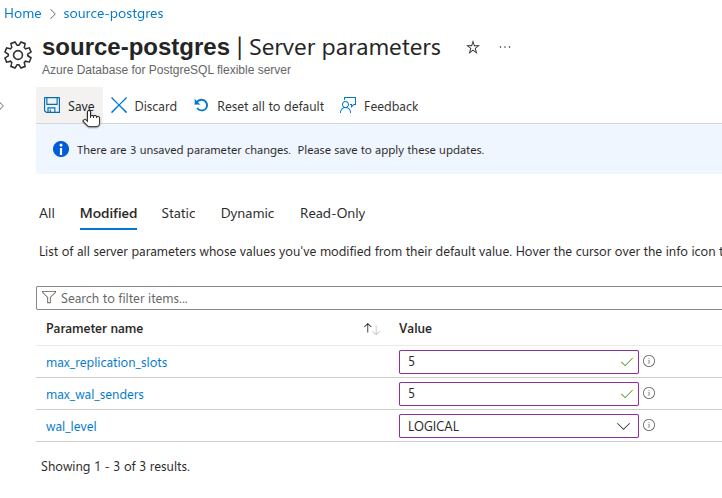
Configure Server Parameters
To support logical replication, you’ll need to adjust a few parameters on your Azure Database for PostgreSQL instance.
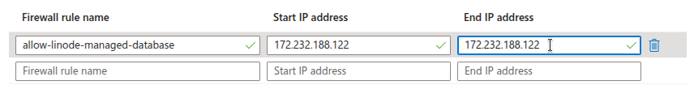
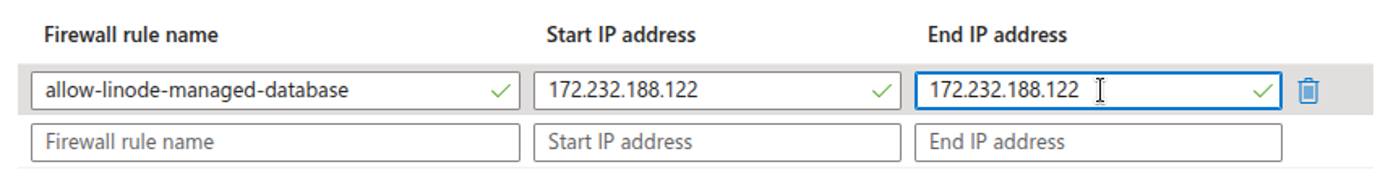
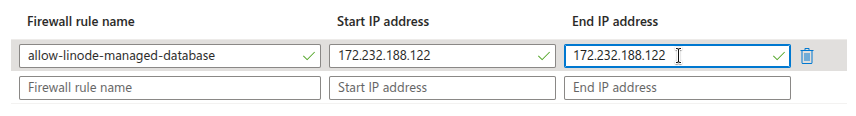
Configure Network Access
Before the Linode Managed Database can connect to your Azure Database instance, ensure that the instance allows network access from the Linode Managed Database.
With network access configured, your Linode Managed Database can reach the Azure Database instance during the subscription creation step in Logical Replication to a Linode Managed PostgreSQL Database.
Create a Replication User
While logical replication can technically be performed using the primary database user, it’s best practice to create a dedicated replication user. This user should have the REPLICATION privilege and SELECT access only to the tables being published.
Follow the steps below to create this dedicated user on your Azure Database instance.
Connect to your source PostgreSQL instance using the
psqlclient. Replace SOURCE_HOST (e.g.,source-database.postgres.database.azure.com), SOURCE_PORT (e.g.,5432), SOURCE_USER (e.g.,azureadmin), and SOURCE_DB (e.g.,postgres) with your own values. You can find the connection details on the Settings > Connect page of your Azure Database instance.psql \ -h SOURCE_HOST \ -p SOURCE_PORT \ -U SOURCE_USER \ -d SOURCE_DBWhen prompted, enter your SOURCE_PASSWORD (e.g.,
thisismysourcepassword).Run the following commands from the source
psqlprompt. Replace REPL_USER (e.g.,linode_replicator) and REPL_PASSWORD (e.g.,thisismyreplicatorpassword) with your own values. For simplicity, this example assumes a public schema and three sample tables (customers, products, and orders). Replace the table names with your actual schema as needed.Source psql PromptCREATE ROLE REPL_USER WITH REPLICATION LOGIN PASSWORD 'REPL_PASSWORD'; GRANT SELECT ON customers, products, orders TO REPL_USER;CREATE ROLE GRANTYou can also grant privileges on all tables with the following command:
Source psql PromptGRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO REPL_USER;GRANT
The newly created user is referenced by the Linode Managed Database when creating the subscription in Logical Replication to a Linode Managed PostgreSQL Database.
Create a Publication
A publication defines which tables and changes (e.g., INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE) should be streamed to the subscriber. At least one publication is required for logical replication, and the subscriber must have matching tables with compatible schemas for replication to succeed.
While still connected to your source database via the
psqlclient, use the following command to create a publication. Replace PUBLICATION_NAME (e.g.,my_publication) and the specific tables you want to replicate (e.g.,customers,products, andorders):Source psql PromptCREATE PUBLICATION PUBLICATION_NAME FOR TABLE customers, products, orders;CREATE PUBLICATIONYou can also create a publication for all tables in the database:
Source psql PromptCREATE PUBLICATION PUBLICATION_NAME FOR ALL TABLES;Run the following command to view all existing publications:
Source psql PromptSELECT * FROM pg_publication_tables;pubname | schemaname | tablename | attnames | rowfilter ----------------+------------+-----------+-------------------------------------------------------+----------- my_publication | public | customers | {customer_id,name,email,created_at} | my_publication | public | products | {product_id,name,price,created_at} | my_publication | public | orders | {order_id,customer_id,product_id,quantity,created_at} | (3 rows)Type
\qand press Enter to exit the sourcepsqlshell.
Your Azure source database is now ready for logical replication. Return to Logical Replication to a Linode Managed PostgreSQL Database to configure the Linode Managed Database and create the subscription.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on